Will Banks Raise Interest Rates Ever Again Reddit
Monetary Policy Objectives
Bank Indonesia is mandated with creating and maintaining rupiah stability. That mandate is explicitly stipulated in Act No. 23 of 1999 concerning Bank Indonesia, as amended by Act No. 3 of 2004 and Human action No. 6 of 2009 in Article 7. Rupiah stability encompasses two dimensions. First, rupiah stability is the price stability of goods and services, equally reflected by aggrandizement. The 2d dimension relates to rupiah commutation charge per unit stability against other currencies. Indonesia implements a gratuitous-floating exchange charge per unit government and substitution rate stability is necessary to achieve and maintain price and financial system stability.
In pursuit of its mandate, Bank Republic of indonesia adopted the Inflation Targeting Framework (ITF) as its monetary policy framework on 1st July 2005. ITF is relevant for the mandate and institutional arrangements mandated in prevailing laws. Based on ITF, aggrandizement is the overriding objective. Nonetheless, Banking company Indonesia continues to refine its monetary policy framework based on the irresolute dynamics and economical challenges faced in order to increment effectiveness.
Monetary Policy Framework
In the implementation of monetary policy, Bank Indonesia applies an Aggrandizement Targeting Framework (ITF). ITF is a framework of publicly announcing an inflation target corridor and adjusting budgetary policy to attain that target as part of the delivery and accountability of the key depository financial institution. In practice, ITF is implemented using a policy rate as a bespeak of budgetary policy and the interbank rate equally the operational target. The Inflation Targeting Framework was formally adopted by Bank Indonesia on 1st July 2005, replacing base coin every bit the target of monetary policy.
Based on experience from the Global Financial Crisis in 2008/2009, an important lesson that emerged was the need for adequate key bank flexibility in response to more than complex economical developments and a stronger fiscal sector influence on macroeconomic stability. Consequently, Bank Indonesia strengthened the ITF framework through its development into Flexible ITF.
What is Flexible ITF?
Flexible ITF was developed around the core elements of the existing Aggrandizement Targeting Framework (ITF), including a publicly announced aggrandizement target and forward-looking monetary policy, namely monetary policy oriented towards achieving the inflation target in future periods due to the time lag consequence of monetary policy.
Public accountability of monetary policy remains an inherent chemical element of Flexible ITF. Flexible ITF was developed based on the following five core elements:
- Aggrandizement targeting every bit the central strategy of budgetary policy.
- Integration of monetary and macroprudential policies to strengthen policy transmission and maintain macroeconomic stability.
- The role of substitution charge per unit and capital flow policies to support macroeconomic stability.
- Strengthening policy coordination between Banking concern Indonesia and the Government to control aggrandizement as well as maintain budgetary and financial organisation stability.
- Strengthening the policy communication strategy every bit a policy instrument.
Why Flexible ITF?
The Global Financial Crisis that occurred in 2008-2009 forced central banks to rescue the economy and maintain fiscal system stability. Furthermore, policies that focused solely on ITF implementation were no longer considered sufficient due to the narrow budgetary policy mandate of maintaining inflation in line with the target corridor, which was insufficient to maintain overall economical arrangement stability.
The role of the fiscal organisation in the economic system is increasing, with the impact of fiscal system instability condign more pregnant. This is reflected in the massive recovery costs and far-reaching affect of the Global Fiscal Crunch in 2008/2009. Such weather condition raised awareness of the critical central bank role to maintain fiscal system stability. Consequently, ITF implementation to maintain cost stability was necessary but not sufficient.
After the Global Fiscal Crisis, withal, growing need emerged for fundamental banks to strengthen financial system stability in order to ensure macroeconomic and financial sector stability. To that end, successful ITF implementation required support of a macroprudential regulatory framework. Therefore, Bank Indonesia evolved ITF into Flexible ITF by strengthening its mandate to maintain price stability and support financial organisation stability.
How is Flexible ITF Practical?
The overriding objective of ITF and Flexible ITF are the same, namely to control inflation. Notwithstanding, a nascent dimension that emerged from the Global Financial Crisis was the central bank'south integrated role to maintain financial organisation stability, while achieving the price stability mandate. The embodiment of Flexible ITF is the flexibility to integrate monetary and fiscal system stability through a policy mix of budgetary, macroprudential, exchange rate and capital period instruments, while strengthening the institutional arrangements in social club to optimise the role of policy coordination and advice.
In accordance with the inflation targeting strategy, Banking concern Indonesia announces the inflation target for a specific future period. The inflation target is ready by the Government in coordination with Bank Republic of indonesia for the upcoming three years through a Minister of Finance Regulation (PMK). Bank Indonesia regularly evaluates whether the inflation projections remain in line with the target corridor ready. The projections are based on several models and the various information available that draw inflation conditions moving frontward as the basis for the monetary policies instituted. This is due to the implications of the fourth dimension lag effect of budgetary policy, with the monetary policy target thus based on future inflation projections. Efforts to reach the target are implemented through a policy mix response based on transparency and accountability.
Bank Republic of indonesia regularly reports the implementation of its duties to the People'due south Representative Council (DPR) and also the Government. Furthermore, Bank Indonesia also routinely publishes assessments of the latest inflation atmospheric condition and outlook moving forward, the decisions taken every bit well equally future policy direction to maintain inflation in line with the target (forward guidance). This is not only washed nether the auspices of transparency, yet too an of import attribute of strengthening Bank Indonesia credibility to ensure policy effectiveness.
To strengthen the effectiveness of monetary policy transmission, Bank Indonesia gear up the BI 7-Day (Reverse) Repo Rate as the policy rate on 19th Baronial 2016, representing the monetary policy response bespeak in terms of controlling aggrandizement in line with the target corridor. Utilise of BI7DRR as the reference rate is role of Banking company Indonesia's monetary policy reformulation.
Previously, Depository financial institution Indonesia had used the BI Rate as the reference charge per unit, equivalent to a 12-month involvement rate in the term structure of monetary operations. Through the BI7DRR, however, the tenor of the monetary instrument was shortened to seven days, which is expected to advance budgetary policy transmission and steer inflation towards the target corridor.
There were three main objectives of monetary policy reformulation. Commencement, strengthening the point of budgetary policy management. Second, strengthening monetary policy transmission effectiveness through its impact on involvement rate movements in the money market place and cyberbanking manufacture. Third, accelerating financial market deepening, especially in terms of transactions and formation of the involvement charge per unit construction in the interbank money market place for tenors of 3-12 months.
In do, budgetary policy reformulation upholds iv salient principles. First, reformulation does non modify the monetary policy framework every bit Banking company Indonesia continues to apply flexible ITF. 2d, reformulation does non change the current monetary policy stance. Third, reformulation ensures the policy rate is reflected in monetary instruments and is transactable with Depository financial institution Republic of indonesia. 4th, determination of the operational target based on diverse considerations can exist influenced by the policy rate. Consistent with the 2d principle, reformulation does non change the current budgetary policy stance because both the BI Rate and BI7DRR are role of the same term structure with regards to guiding inflation towards the corresponding target.
The implementation of Flexible ITF also aims to achieve fiscal organisation stability. To that end, Flexible ITF implementation is supported by the awarding of macroprudential policy. Macroprudential policy focuses on the interactions between fiscal institutions, markets, infrastructures and the broader economy, including measurement of futurity potential gamble. Such policy aims to preclude systemic take a chance that could trigger a fiscal system crisis due to macroeconomic weather. An in-depth explanation of macroprudential policy is bachelor at the post-obit link: (Link ke kebijakan makroprudensial).
Flexible ITF implementation is also supported by exchange rate policy. Bank Indonesia institutes exchange rate policy in gild to manage rupiah exchange rates in line with the currency's fundamental value and marketplace mechanisms. Furthermore, exchange rate policy aims to reduce shocks that emerge from a demand and supply mismatch in the strange exchange market through selling intervention in the spot market place, Domestic Non-Deliverable Forrad (DNDF) market place an FX futures marketplace too equally through purchases of tradeable government securities (SBN) in the secondary market. This strategy simultaneously maintains exchange rate stability an acceptable rupiah liquidity.
The various aforementioned policies are strengthened through policy coordination with the Government, particularly on the supply side. Government policy is predominantly oriented towards maintaining affordable prices, uninterrupted supply and distribution too as effective advice in order to stabilise nutrient prices and control inflation. Policy coordination between Bank Indonesia and the Government to control inflation has been strengthened through the establishment of a National and Regional Inflation Task Forces (TPI). In addition, policy coordination also reinforces financial system stability. Through the Financial System Stability Committee, Bank Republic of indonesia in conjunction with the Ministry of Finance, Indonesian Financial Services Authority (OJK) and Deposit Insurance Corporation (LPS) determine which coordination measures are necessary and provide recommendations in terms of monitoring and maintaining fiscal organisation stability.
The overriding objective of monetary policy is to create and maintain rupiah stability, every bit reflected by low and stable inflation. To that end, Bank Indonesia sets the BI 7-24-hour interval (Reverse) Repo Rate as the main policy musical instrument that influences economic activeness, with inflation every bit the ultimate goal. The procedure of setting the BI7DRR to achieving the inflation target is transmitted through various channels with a time lag.
Adjusting the BI7DRR to influence inflation is known as the budgetary policy transmission mechanism. This mechanism shows how Bank Indonesia policy, through adjustments to budgetary instruments and the operational target, influences various economic and fiscal variables before ultimately affecting inflation. The machinery works through interactions between the central bank, banking industry and financial sector, likewise as the real sector. Adjustments to the BI7DRR influence aggrandizement through diverse channels, including the interest rate channel, credit channel, substitution rate channel, nugget cost aqueduct and expectations channel..
In terms of the interest charge per unit channel, adjustments to the BI7DRR influence deposit rates and lending rates in the banking industry. Banking company Indonesia can utilise tight-bias monetary policy past raising interest rates, which impacts aggregate demand and alleviates inflationary pressures. In dissimilarity, reducing the BI7DRR will lower lending rates thus increasing corporate and household demand for loans. In addition, lower lending rates also reduce the cost of upper-case letter for investment in the corporate sector, thus stoking consumption and investment activity and stimulating the economy..
Adjustments to the BI7DRR can too influence the substitution charge per unit through the exchange rate channel. A hike in the BI7DRR, for example, would increase the differential between involvement rates in Indonesia and other countries. A wider involvement charge per unit differential would attract not-resident investors to identify uppercase in financial instruments in Indonesia seeking a higher rate of return. In turn, the foreign capital inflow would trigger rupiah appreciation, leading to cheaper imports and more expensive, or less competitive, exports from Indonesia, thus stimulating higher imports while simultaneously reducing exports. Consequently, rupiah appreciation would ease inflationary pressures.
The bear on of changes in interest rates on economic activity also influences public inflation expectations through the expectations channel. Lower interest rates stimulate economic activity an increment inflation, with workers thus anticipating higher aggrandizement and, hence, demanding higher wages. Producers subsequently pass on the toll of college wages to consumers by raising prices.
The budgetary policy transmission mechanism is characterised past a variable time lag. The time lag associated with each transmission aqueduct is different. Under normal conditions, the banking manufacture volition answer to increases/decreases in the BI7DRR by raising/lowering interest rates. Notwithstanding, if the banking industry detects higher risk in the economy, the response to a down BI7DRR movement is slower. In improver, in the instance of banking manufacture consolidation to increase capital letter, lower lending rates and increasing need for loans do non necessarily increase bank lending in response. On the demand side, consumers may non necessarily respond to lower lending rates in the banking industry through higher demand for loans if the economic outlook is weak. Therefore, the effectiveness of monetary policy transmission is affected by external conditions, the financial sector and banking manufacture, besides as the real sector.

Transparency and Advice
In accord with Act No. 23 of 1999 concerning Bank Indonesia, as amended past Act No. 3 of 2004 and Act No. 6 of 2009, Article 4, Paragraph 2 states that Banking concern Indonesia is an contained institution, free from government and tertiary-party interference, unless explicitly stipulated in prevailing laws and regulations. Institutional independence is balanced against transparency and accountability.
Transparency
The principles underlying monetary policy transparency ensure that the information communicated allows the public to empathise and conceptualize the decisions taken by the central bank to achieve the overriding objective. Therefore, the purview of information communicated to the public is every bit follows:
- Objective
The fundamental bank explicitly and consistently communicates what is to exist achieved past monetary policy in terms of the overriding and curt-term objectives, also equally the rationale behind those objectives. - Method
Primal banking company transparency in relation to procedural activities in budgetary policy, including communicating the budgetary operations undertaken, the results of economical modelling and projections as well as the bones assumptions used, in guild to course expectations in the financial markets as well every bit prevent and minimise market place shocks. In addition, this is required to enhance public understanding of the central bank's budgetary policy. - Decision Making
The central depository financial institution announces the policies taken along with the underlying considerations, such as a decision to heighten the policy rate, immediately after the decision has been made.
In addition, the scope of transparency in monetary policy is as well contained within the "Lawmaking of Expert Practices on Transparency in Monetary and Financial Policies", which has been developed by the International monetary fund (Imf) since 1999 and is currently applied by many of its members. The Code contains a number of key skillful practices as follows:
- Clarity of roles, responsibilities and objectives of the budgetary policy authority;
- Open process for formulating and reporting monetary policy decisions;
- Public availability of information on monetary policy; and
- Accountability and assurances of integrity by the monetary authority.
Monetary Policy Advice
Monetary policy effectiveness can be improved through constructive communication, especially during periods of heightened uncertainty. As the monetary authority, Bank Indonesia but has direct influence over short-term interest rates, while long-term interest rates are determined more by future expectations of monetary policy, which can be directed through policy communication.
Communication contributes to stronger transparency and accountability at Bank Republic of indonesia by providing greater public understanding in terms of monetary policy in full general, while forming public and market place expectations besides as reducing future incertitude. Banking company Indonesia conducts monetary policy communication through various media as follows:
- Press Releases and Press Conferences;
- Publications, including the Monetary Policy Study, Monetary Policy Review, Economical Report on Indonesia, Quarterly DPR Report and then on;
- Banking concern Indonesia website also equally diverse digital and social media platforms;
- Talk shows aired on radio and television;
- Seminars and discussions with stakeholders; and
- Regional dissemination.
Accountability
Human action No. 23 of 1999 apropos Bank Republic of indonesia, as amended past Act No. 3 of 2004 (every bit amended by Human activity No. six of 2009), mandates accountability at Banking concern Indonesia in the implementation of duties, responsibilities and budget.
PThe principles of accountability in terms of implementing Bank Indonesia's duties and responsibilities are practical through the direct public communication of information via the mass media at the get-go of each year concerning an evaluation of monetary policy implementation in the previous year also as the monetary policy management and targets for the upcoming year. Furthermore, such information is besides communicated in writing to the President and People's Representative Council (DPR) of the Republic of Indonesia.
Accountability also closely relates to independence. More independence enjoyed by a central depository financial institution demands greater accountability.
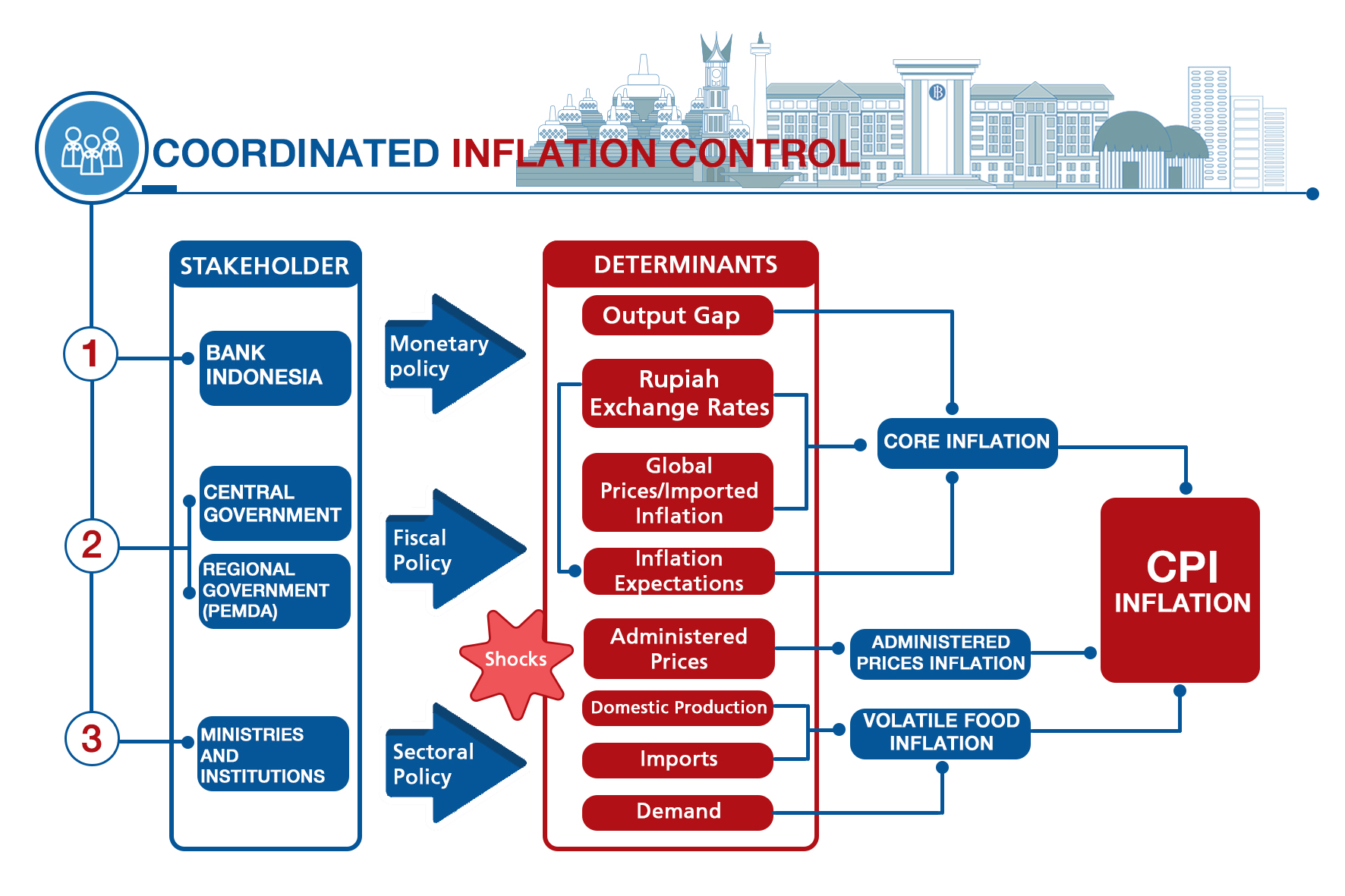
Low and stable aggrandizement are prerequisites for public prosperity in line with the macro policy goals. Nevertheless, sources of inflationary pressures non only originate from the need side, which tin be managed by Bank Indonesia, just also stem from the supply side in relation to the product and distribution of goods. In addition, inflation shocks may also emerge due to government policy concerning administered prices, such equally fuel and other energy prices. Therefore, a policy mix is required in order to accomplish low and stable inflation.
Bank Indonesia coordinates with the central and local authorities to control inflation. Meanwhile, the Regime also plays a part in terms of decision-making inflation expectations and managing supply through the management of supply, distribution, connectivity, trade chain and subsidies. Synergy is formed to control inflation within the predetermined target corridor through the establishment of inflation task forces. A central inflation chore force (TPI) was established in 2005, with regional aggrandizement task forces subsequently formed since 2008.
Coordinated inflation control was strengthened through Presidential Regulation (Perpres) No. 23 of 2017 concerning the National Inflation Chore Force (TPIN) as a legal foundation. The Presidential Regulation stipulated the coordination mechanism for inflation control through the formation of a Central Aggrandizement Task Force (TPIP), besides as Regional Inflation Chore Forces (TPID) at the provincial and city/regency level.
The legal foundation was later on bolstered by a promulgation of Coordinating Minister of Finance Regulation No. ten of 2017 concerning the Mechanisms and Procedures for TPIP, Provincial TPID and Metropolis/Regency TPID, Coordinating Minister of Finance Regulation No. 148 of 2017 concerning the Duties and Membership of Working Groups and TPIP Secretariat, and Minister of Home Diplomacy Prescript No. 500.05-8135 of 2017 concerning the Regional Inflation Task Forces (TPID). The inflation control plan focuses on 4K principles as follows:
- Affordable prices.
- Available supply.
- Uninterrupted distribution.
- Effective communication.
Source: https://www.bi.go.id/en/fungsi-utama/moneter/default.aspx
0 Response to "Will Banks Raise Interest Rates Ever Again Reddit"
Post a Comment